
我们看到极端天气导致北美天然气和电力市场(例如德克萨斯州)出现多次复合故障,那里的供应、需求和价格平衡受到冲击,管道和液化天然气出口的减少在全球产生了连锁反应。 伴随天气事件,全球能源政策因气候变化问题而发生转变,导致全球天然气和液化天然气市场充满不确定性。
为了应对这些变化,路孚特和 RBAC 将一套全新的天气情景以及天然气和液化天然气基建假设、政策、成本和约束方面的大量变化纳入了 RBAC 的 G2M2 ®全球天然气预测分析系统™,针对全球天然气市场进行了全面和客观的模拟分析。 本报告详细介绍了美国、欧洲和亚洲市场不断变化的动态,帮助您为未来的任何动荡天气做好准备并渡过难关。
简介:
2020年秋季,RBAC和路孚特初次合作开发了多个场景,围绕即将到来的2020/2021年冬季的天气和其他天然气市场动态。 此次合作发表的天然气前景引起了业界的极大关注,但是2020/2021年的实际冬季的影响要比预测的场景大得多。 基于北极寒流模拟的结果更严重,破坏力更大。 储气量被拉低到危险的低水平,全球天然气市场在2021年迅速升温。随着2021/2022年冬季的临近,RBAC和路孚特-RBAC发布2021年全球短期天然气和液化天然气市场展望,为北半球即将到来的取暖季节提供有价值的参考。
RBAC 团队利用 G2M2® 开发了总计36 个月的预测,利用市场基本面因素和天气敏感性探索区域市场之间的互连。该团队利用19种场景来评估天气对全球天然气平衡的影响,以及北美、欧洲和亚洲枢纽的价格。
此文希望分享今年展望的重要内容,并将今年与去年的预测进行客观的比较和分析,借以提高我们对市场模拟的理解。
亨利港(Henry Hub)价格对液化天然气出口的影响
当我们回顾2020-2021年Refinitiv-RBAC全球短期天然气和液化天然气市场展望(于2020年11月发表)时,其中重要的见解包括以下几个方面:
• 冬季需求可能是亨利港 2020 年第 4 季度和 2021 年第 1 季度价格的主要驱动因素之一。美国冬季需求强劲,可能会使天然气留在国内,而不是作为液化天然气运往海外。
• 在后 COVID 世界中,生产商将被迫在管理短周期生产方面更加灵活,而不是为了实现更积极的增长而花费更多现金。
• 欧洲和亚洲的国内需求都依赖于液化天然气进口,但对区域价格的影响不同。
但是与实际情况相比其研究的20个天气情景(根据过去20年的数据)缺少大幅波动的情况。由于模型的假设不够极端,无法推动产生G2M2®全球天然气预测分析的现货价格飙升、需求冲击和供应减少,以接近实际发生的冬季天气条件。
2021 年 2 月,北美的情况尤其如此(请参阅下图,请注意右上图的纵坐标轴的价格是左上图的两倍)。去年报告中运用的情景、数据和模拟条件未能充分考虑北美主要产区电力和天然气管网的过冬准备不足以及由此对液化天然气出口造成影响的未知因素。
图表1 - 2020/2021亨利港(Henry Hub)价格和美国液化天然气出口预测
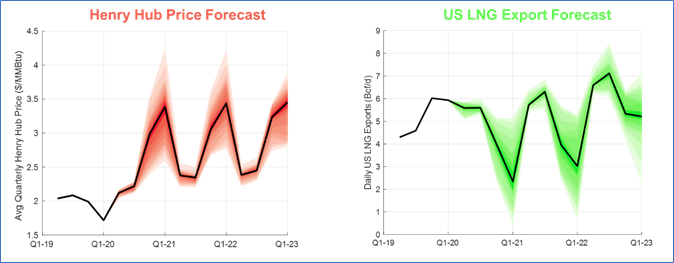
图表 2 - 2021/2022 (Henry Hub)亨利枢纽价格和美国液化天然气出口预测
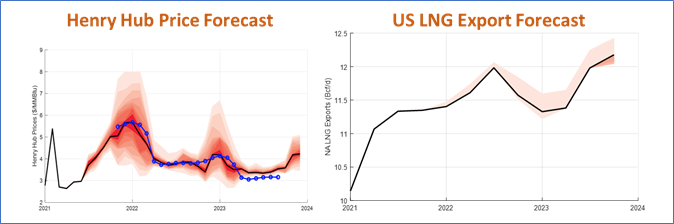
该研究的2021-2022年展望显示,2022年亨利港的年平均价格上升至5.50美元/MmBtu左右,而去年的报告为3.50美元/MmBtu。 此外,与去年的预测相反,今年美国液化天然气出口预计运行接近100%的产能。
一般认为,随着(美国)国内天然气价格的上涨,液化天然气出口将减少,因为国内市场将产生更大的利润潜力。 然而,情况并非如此,因为全球天然气和液化天然气价格飞涨,供应短缺,同时欧洲冬季来临之际,储存水平低于正常水平,因此欧洲市场的利润空间可能会更大。
全球天然气和液化天然气价格
由于全球供应限制继续影响天然气和液化天然气市场,基于使用G2M2®的各种天气情景,该报告预测出美国液化天然气出口的价格差大于5美元/MMBtu。
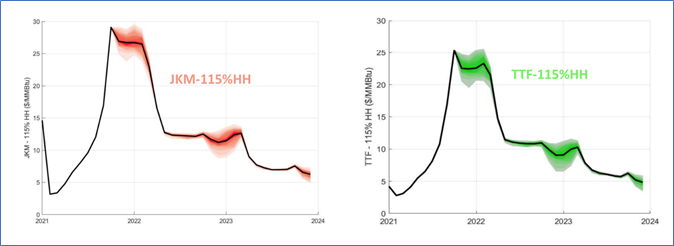
图表3 - 2021/2022 JKM 和TTF的价格
欧洲天然气市场 - TTF 价格驱动因素
欧洲存储:
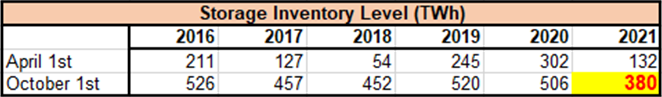
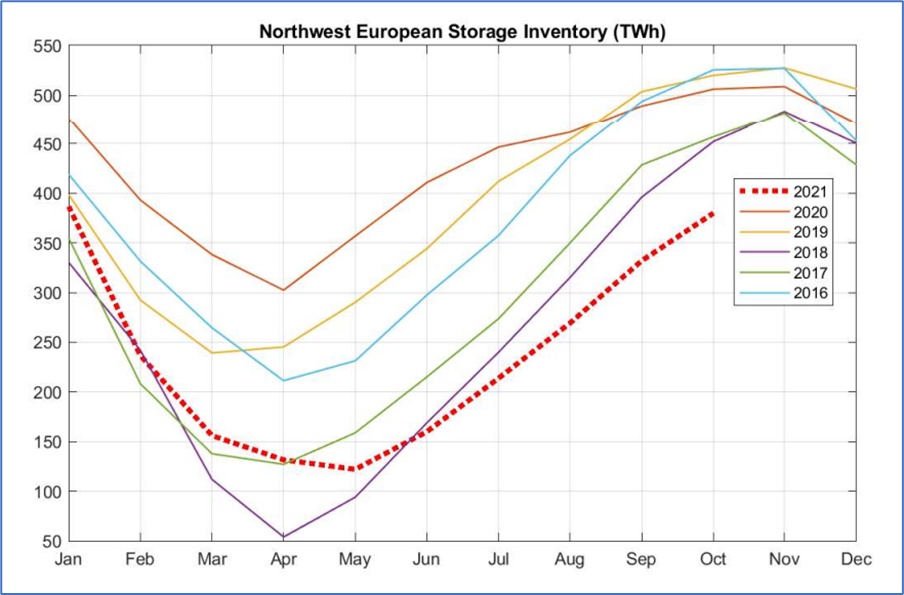
不论是在冬季或异常炎热的夏季,欧洲的储气库库存一直相对来说较为稳定。然而,创纪录低值的欧洲西北部地下存储库存给TTF价格带来了巨大的上行压力。 在过去 5 年中,从 NWE 存储的冬季提取的天然气量从 2018-19 年温和冬季的 210 TWh 大幅转向 2017-18 年非常寒冷的冬季的 400 TWh。2020/2021年冬季接近正常天气条件,但存储水平下降了380 TWh。
图表 4 - 欧洲存储库存水平
2020/2021年冬季,由于亚洲需求在异常寒冷的冬季增加,液化天然气进口供应减少,导致液化天然气进口量高于正常水平。液化天然气的发送量为20Bcm(220 TWh),低于前一年的33Bcm(360 TWh)。
2021 年 6 月初,欧洲存储库存为 160 TWh 或容量的 30%,为过去 5 年(2016-2020 年)的最低水平,明显低于 64% 的五年平均水平。同时今年注气延迟了将近一个月。直到5月才开始注气,而从历史上看,注气是在4月份开始的。
图表 5 – 欧洲西北部地下储气库情况
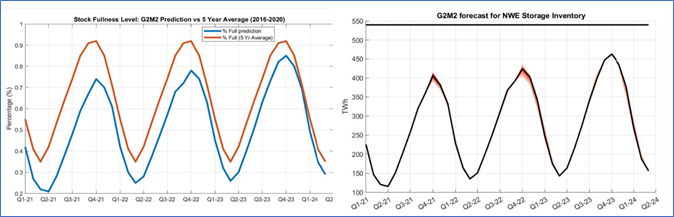
研究团队使用的 G2M2 模型基于 19 种天气情景,包括多种不同的需求预测。这些方案的结果表明,预计今年冬季(10月-3月)欧洲西北部大约230 TWh的天然气将被取出。
在2021年-2022年的冬天,该模型预测存储水平约为 135 TWh 或存储容量的 25%。相比之下,5年的平均值为35%。预计明年欧洲西北地区存储库存水平将继续低于5年平均水平,直到2023年底才能赶上5年平均水平。
图表 6 - G2M2 欧洲存储库存水平
从俄罗斯进口:
尽管欧洲大部分国家都在积极地进行能源转型,但其天然气市场仍严重依赖天然气和液化天然气的进口,已满足国内需求。进入欧盟国家的天然气主要通过俄罗斯、挪威和北非的管道以及来自世界各地的液化天然气罐车输送。
近几个月来,俄罗斯对欧洲天然气供应的不确定性对TTF价格产生了重大影响。欧洲市场对天然气供应变化的任何迹象的反应仍然非常强烈。在下图中,当出现新的有关北溪二号的事件和公告,例如政策变化和容量拍卖结果等,价格都会有所波动。
图表 7 – 北溪二号相关事件和公告对价格的影响

欧洲天然气生产:
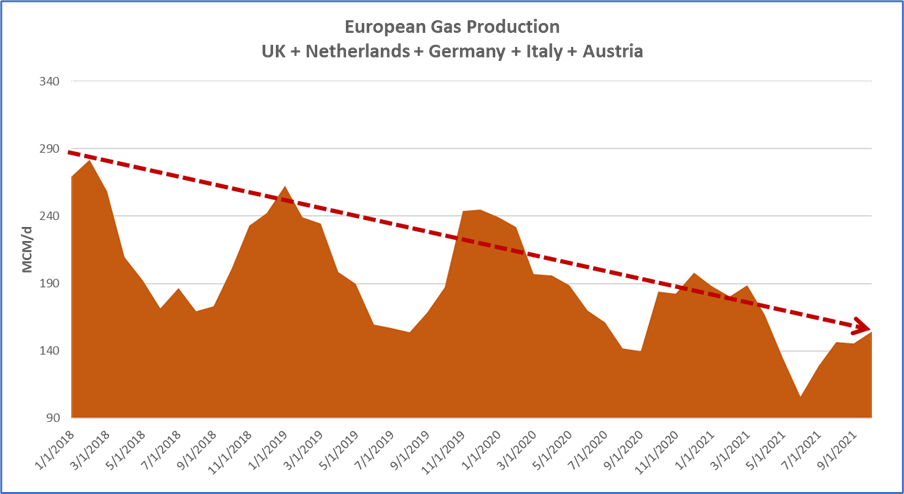
欧洲天然气产量继续下降,进一步加剧了TTF价格的上行压力。自 2018 年 1 月以来,欧洲每日天然气产量从大约 2.8亿降至1.6亿立方米。由于能源转型的目标已经确定,没有迹象表明欧盟国家将大力开发国内的七天。为了稳定价格,欧洲需要找到一种方法已保证更多的天然气的稳定供应,而在这个不确定的时期,形势仍然不算明朗。
图表 8 - 欧洲天然气生产
主要结论
使用 RBAC的G2M2®全球天然气预测分析系统基于各种天气情况下模拟不同场景,我们发现了一些重要结论,在考虑未来冬季市场的基本时,需要加以评估。
• 与往常一样,天气是最大的未知数和风险之一。
• 鉴于目前全球天然气市场的紧张状况,北半球任何大型市场(美国、欧洲或亚洲)的冬季都比正常寒冷,这将导致主要枢纽价格进一步走高,主要天然气市场可能会在冬季面临短期风险。
• 如果今年冬天异常寒冷,需求量将大幅增加,区域内的断电可能是不可避免的。
此外,由于各国需要更长的时间来补充其地下储气的库存,这意味着全球天然气市场的紧张状态将持续更长的时间。
• 中国、南美洲等国家的需求增长可能会加剧目前市场的紧张,迫使亚洲和欧洲客户争夺相同的液化天然气气源。
• 欧洲进口俄罗斯的管道天然气总量将继续受到限制,影响因素仍在于北溪二线何时能正式投产。
• 关于北溪二线,由于其认证流程等因素,预计启动日期已经出现一些延迟,这是管道正式投入使用和开始商业流之前的最后一步。除其他事项外,认证过程受到美国制裁和波兰反对,而且启动手续耗时长,无法满足在原定的2021年10月1日开始日期。从9月初管道运营商向德国监管机构提交申请开始,认证过程预计需要6-8个月才能完成。在本次研究中的假设是北溪二线于2022年第一季度末开始正式投入商用。
• 另一个风险是,一旦投入使用,北溪二号需要多长时间才能增加交货量。迄今为止,俄罗斯尚未承诺通过新的预计路线向欧洲输送多少天然气。基于这种情况,欧洲进口俄罗斯的管道天然气总量仍将受到限制。
结论
冬天总是会以这样或那样的方式处理影响市场的不可预知的情况。 能源转型期间需求持续增长和供应紧张将给整个北半球的价格带来上行压力。 使用本研究中所做的市场模拟,可以快速分析各种潜在假设和情景展望,以确定一系列可信的结果,以便做出正确的决策,实现组织的目标,包括能源过渡所要求的目标。
RBAC公司创立于1987年,主要负责开发和维护是全球和区域天然气和液化天然气市场预测系统,其利用数学建模、统计分析、数学算法开发和数据库设计方面等专业知识向能源行业公司以及涉及能源、交通和环境的政府机构提供强大的分析工具。G2M2®全球天然气预测分析系统™专为全球天然气市场的融合开发方案而设计。它是一套完整的模型系统,用于预测全球天然气市场的天然气和液化天然气生产、运输、储存和消费。欲了解更多信息,请访问:https://rbac.com/
James Brooks, Ning Lin, Xin Tang
Background:
When caught in a heavy storm there is a natural reaction to go into a mode of coping to the situation. That coping may get you through the storm but could have long term unexpected ramifications. Since the release of last year’s Refinitiv-RBAC 2020/2021 Winter Outlook a lot has changed in energy economics, operations, trade and infrastructure.
We have seen extreme weather drive multiple compound failures in the North American gas and power markets (e.g. Texas), where supply, demand and price balances were shocked and a reduction in exports by pipeline and LNG created ripple effects across the globe. Along with weather events, a shift in global energy policy due to climate change concerns has contributed to the uncertainty swirling around gas and LNG markets around the world.
To deal with these changes, Refinitiv and RBAC have incorporated a whole new set of weather scenarios along with numerous changes in gas and LNG fundamentals, policies, costs and constraints into RBAC’s G2M2® Market Simulator for Global Gas and LNG™, in order to produce an updated outlook for the 2021/2022 winter season. This report gives a detailed look at the changing dynamics of the U.S., European and Asian markets and delivers real insights to help you prepare for and get through any tumultuous weather ahead.
Introduction:
In the Fall of 2020, analysts at RBAC and Refinitiv partnered to develop several scenarios around the upcoming 2020/2021 winter season’s weather and other gas market dynamics. Simulations using G2M2 yielded several impactful insights including:
· Winter demand would likely be one of the primary drivers for Henry Hub price for 2020 Q4 and 2021 Q1. Strong US winter demand would likely keep gas at home rather than being sent overseas as LNG.
· In a post-COVID world, producers would be forced to be more flexible in managing short-cycle production, rather than outspending cash to achieve more aggressive growth.
· Europe and Asia domestic demand would both rely on LNG imports but influence its regional price differently.
This initial joint gas outlook generated a great deal of attention from the industry. But the actual winter of 2020/2021 had a far greater impact. Arctic blasts were more severe and more damaging than the results of all scenarios the team simulated. Gas storage was drawn down to dangerously low levels. As a result global gas markets have heated up to prepare for this coming winter. With the 2021/2022 winter season approaching, the RBAC and Refinitiv team has rededicated its efforts to producing a winter gas outlook for the coming heating season in the northern hemisphere.
Like in the previous study, the Refinitiv-RBAC team developed a series of 36 month forecasts using G2M2, exploring the interconnection between regional markets using both fundamental drivers and weather sensitivities. The team made runs using 19 different weather scenarios to estimate their impact on the global gas balance as well as prices at hubs in North America, Europe, and Asia.
Impact of Henry Hub Price on LNG Exports
As we look back at the 2020/2021 Refinitiv-RBAC study, the 20 weather scenarios studied (based on the last 20 years of data) predicted a far less tumultuous and volatile winter season than nature delivered. Scenarios were not severe enough to push the simulation to generate spot price spikes, demand shocks and supply reductions approaching those that resulted from winter weather conditions that actually happened.
This was especially true for North America in February 2021 (see lower-left graph below but note the price scale is twice that of the upper left graph). The scenarios, data and simulation conditions could not have included the unknown factors around the unpreparedness of an insufficiently winterized power and gas pipeline network in the key producing region of North America and the resultant impact on LNG exports.
Chart 1 – 2020/2021 Henry Hub Price and US LNG Export Forecast

Chart 2 – 2021/2022 Henry Hub Price and US LNG Export Forecast

The study’s 2021/2022 outlook shows a significant increase in the average Henry Hub price to about $5.50/MmBtu in 2022 compared to $3.50MmBtu in last year’s study. In addition, in contradistinction to last year’s forecast, this year’s study projects LNG exports running close to 100% capacity throughout the forecast.
One might think with the increase in domestic prices for gas one would see a reduction in LNG exports as domestic markets would yield a greater potential for profit. However, that is not the case, as global gas and LNG prices have skyrocketed with supply shortages and lower than normal storage levels on the cusp of winter in Europe.
Global Gas and LNG Price
As global supply constraints continue to impact the gas and LNG markets, regardless of the varied weather scenarios studied using G2M2, the study projects price spreads for US LNG exports well above $5/MMBtu for the coming winter.
Chart 3 – 2021/2022 JKM and TTF Prices

European Gas Market – TTF Price Drivers
European Storage:
Gas storage has always been the market stabilizing factor during the winter season or unusually hot summers. However, record low Northwest European underground storage inventories have put intense upward pressure on TTF prices. Over the last 5 years, the amount of gas withdrawn during winter from NWE storage has swung wildly from 210 TWh during a mild winter of 2018-19 to 400 TWh in a very cold winter of 2017-18. The 2020/2021 winter was near normal weather conditions, but storage levels were down by 380 TWh.
Chart 4 – European Storage Inventory Levels



Imports from Russia:
Although European nations are leading the way in the energy transition, European gas markets still rely heavily on gas and LNG imports to meet domestic demand. Gas imports into the EU are mainly delivered through pipelines from Russia, Norway, and North Africa as well as by LNG tankers from around the world.
In recent months, uncertainty around Russian gas supply to Europe have had a significant impact on TTF prices. The European market continues to be very reactive to any indication of changes to gas supply. For example, there was a very strong reaction to potential changes around Russian supply from the Nordstream 2 pipeline and capacity auction results as you can see in the chart below.
Chart 7 – Price Impact of Supply Events and Announcements

European Gas Production:
Further exacerbating the upward pressure on TTF prices, European gas production has continued to decline. There has been a drop in production from approximately 280 to 160 MCM/D since January 2018. With the targets for the energy transition well established, there is no indication that the EU will bolster domestic production. In order to stabilize prices, it will need to find a way to secure more gas supply, which will prove to be quite difficult in these uncertain times.
Chart 8 – European Gas Production

Key Take-Aways
Running a variety of weather scenarios using RBAC’s G2M2 Market Simulator for Global Gas and LNG has yielded some very important take-aways that need to be evaluated when considering one’s market fundamentals analysis for the upcoming winter season.
· As always, the weather is one of the biggest unknowns and risks.
· Given the current tightness situation in the gas market globally, colder than normal winter in any of the big markets of the Northern hemisphere (US, Europe or Asia) would send major hub prices even higher and leave markets with the risk of a physical gas shortage over the winter months.
· Some blackouts or demand disruptions may be inevitable if demand is unusually high this winter.
· In addition, this also means that the tightness in global gas market will remain for longer as it will take more time for countries to replenish their underground storage stocks.
· Demand growth in other regions (i.e., China, South America) could exacerbate the current tightness in the market forcing Asian and European customers to compete for the same LNG cargoes.
· Europe could expect continuing limited Russia gas supply. When it will begin flowing and how much gas to be expected from Nord Stream 2 is still quite uncertain.
· Regarding the Nord Stream 2 pipeline, there has already been some delay in the expected start date due to its certification process, which is a mandatory final step before the pipeline can be commissioned and start commercial flows. Among other things, the certification process was hampered by American sanctions and opposition from Poland and did not start soon enough to meet the originally scheduled start date of October 1st, 2021. The certification process is expected to take up to 6-8 months to complete from early September when the pipeline operator submitted its application to the German regulator. For this study, the team has assumed it to start flowing by the end of Q1 2022.
· Another risk is how long it will take Nord Stream 2 to ramp up deliveries once it is commissioned. To date, Russia has not committed to any figure on how much gas will be send to Europe via the new projected route. There is a possibility that it may be at limited capacity.
Conclusion
Winter will always deal unpredictable conditions that impact the market one way or another. Continued growth in demand and tight supply during the energy transition will put upward pressure on prices throughout the Northern Hemisphere. Using market simulation such as has been done in this study allows one to quickly analyze a variety of potential assumptions and scenario outlooks to determine a credible range of results in order to make good decisions to achieve an organization’s goals including those demanded by the energy transition.
Team Leads:
RBAC
Dr. Ning Lin, Ph.D. – ning.lin@rbac.com
Dr. Robert Brooks, Ph.D. – robert.brooks@rbac.com
Refinitiv
Nantanaporn Udomchaiporn – nantanaporn.udomchaiporn@refinitiv.com
Xin Tang – xin.tang@refinitiv.com
RBAC Inc. is the market leading supplier of global and regional gas and LNG market simulation systems. These systems provide industry analysts powerful tools for supporting corporate investment and M&A strategy, improving free cash flow, achieving environmental and sustainability goals, including reduction of CO2 emissions, conducting credible and useful risk analysis and planning, and enhancing profitability in commodity trading. Organizations using RBAC’s products and services include energy industry firms and consultants, ISOs and RTOs, and government agencies involved with energy, transportation, and the environment. The G2M2® Market Simulator for Global Gas and LNG™ is designed for developing scenarios for the converging global gas market. It is a complete system of interrelated models for forecasting natural gas and LNG production, transportation, storage, and deliveries across the global gas markets.
Refinitiv, an LSEG business, is one of the world’s largest providers of financial markets data and infrastructure. Serving more than 40,000 institutions in over 190 countries, we provide information, insights, and technology that drive innovation and performance in global markets. Refinitiv Natural Gas and LNG Research teams provide the most comprehensive insights on market developments, price movements and supply/demand forecasts by leveraging sophisticated proprietary modelling and forecasting techniques. Our reports can help you understand the global gas market and empower you to make informed trading decisions. For more information, please visit: https://www.refinitiv.com/en